Partial Locking
Introduction
While the customers face challenges in customizing their applications to meet their unique needs, they are often forced to choose between relying on end-user customizations for their application enhancements or having no room for even minor configuration changes. The existing functionality posed a limitation, for example - relabelling picklist values. Customers are forced to either forgo improvements made by the original developers or accept extremely limited configuration options.
To address these challenges, Infinite Blue Platform has now introduced three types of application lock options:
-
Locked: This setting ensures that the entire application remains untouched in the destination tenant, creating a genuine Software as a Service (SaaS) experience.
-
Partially Locked: Administrators can selectively lock or unlock specific components within an application, offering a balance between customization and control.
-
Unlocked: This option provides complete customization freedom but effectively prevents future upgrade paths or enhancements.
With Partial Locking, Application Publishers/ISV providers can design configurable applications, ensuring customized configurations remain intact during upgrades. With granular control over customization elements and preserving vital integrations with application upgrades. With this mechanism, emergency application updates can also be swiftly deployed without destabilizing the system.
Likewise, the end user can also benefit from a customized environment where components can be tailored effortlessly. They can manage versions effectively, selectively adopt changes, and have the flexibility to decide when to upgrade. This approach ensures a seamless transition while preserving custom settings.
For detailed information, see Partial Lock Preferences.
Use Case
Managing partially locked page sections
This use case outlines the process of managing Page Section configurations where tenant-level customizations persist while still allowing important updates from the source application to be applied.
-
In the source application, the New Employee page contains two sections, with the Employee Details section configured to display in a two-column layout.
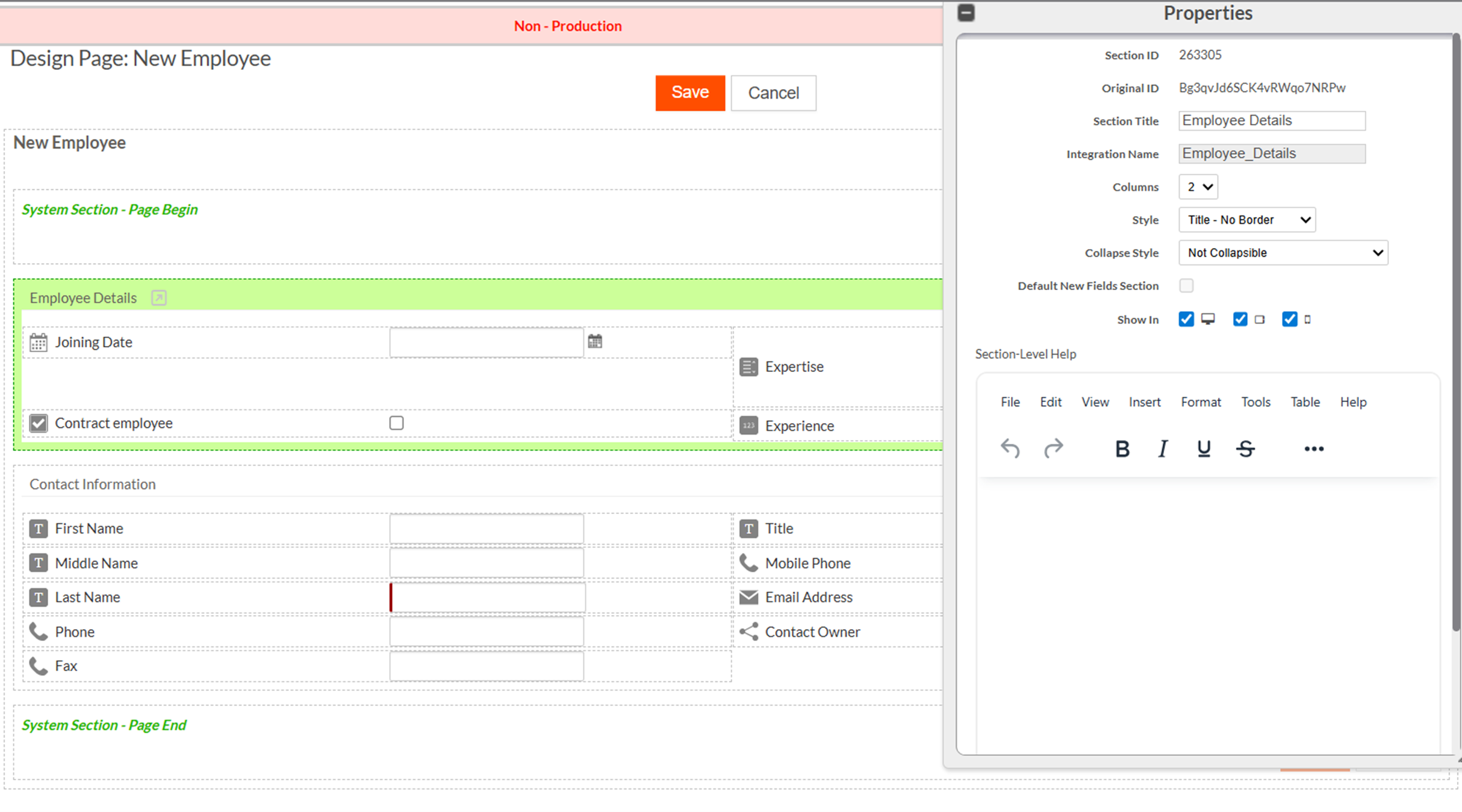
-
When this version is installed in the destination tenant, the tenant customizes the page according to it's own requirements. These changes include renaming the Page title and adjusting the Employee Details section layout from two columns to a single column.
-
After saving these changes, the system marks the affected components with a
Modifiedflag in the components table. A red warning icon also appears in the Page Designer, indicating that local changes exist and that the component is now off the upgrade path for customizable properties.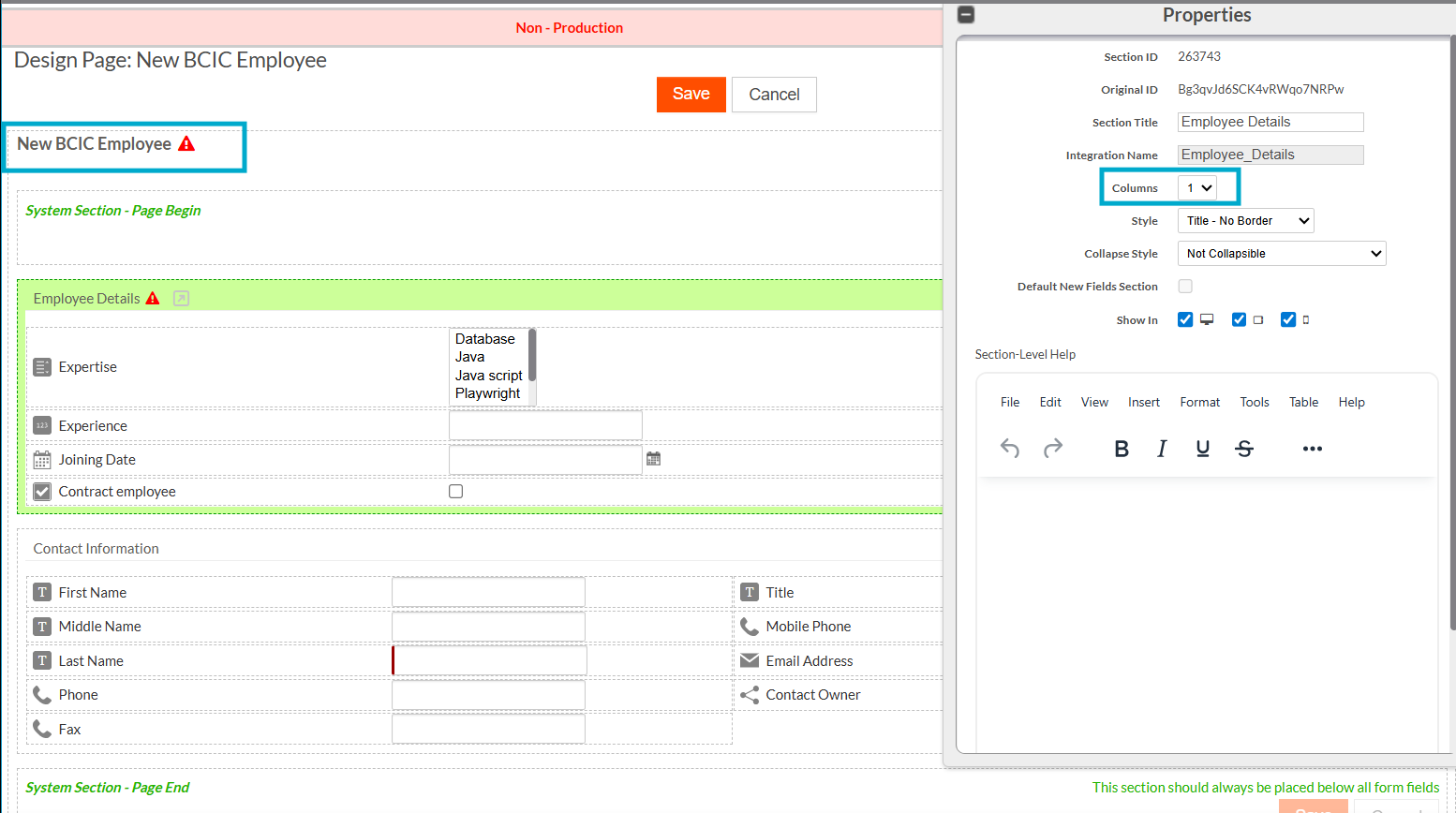
-
However, the tenant has the option to bring the component back onto the upgrade path using the Restore Upgrade Compatibility action. This option is available at the parent page level - restoring all tabs, sections, and cells - or at the individual section level in the sections table. Once the Restore Upgrade Compatibility action is triggered, the
Modifiedflag is reset to false, although the restoration takes effect only after the next application upgrade.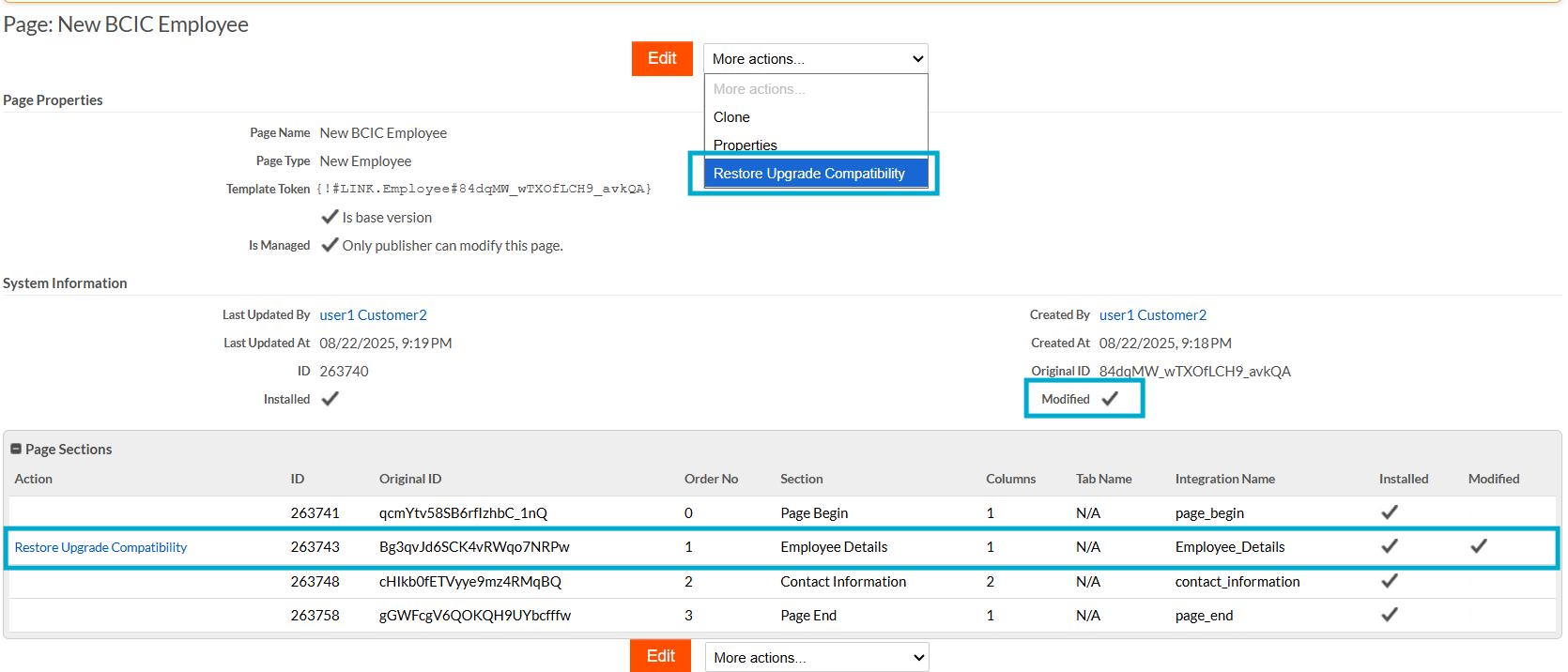
-
Meanwhile, the source application tenant modifies the same page by renaming the Page Title, updating the Section Title, changing the Section Integration Name, adding Section Help Text, and introducing new fields such as WFH and Location into both sections.
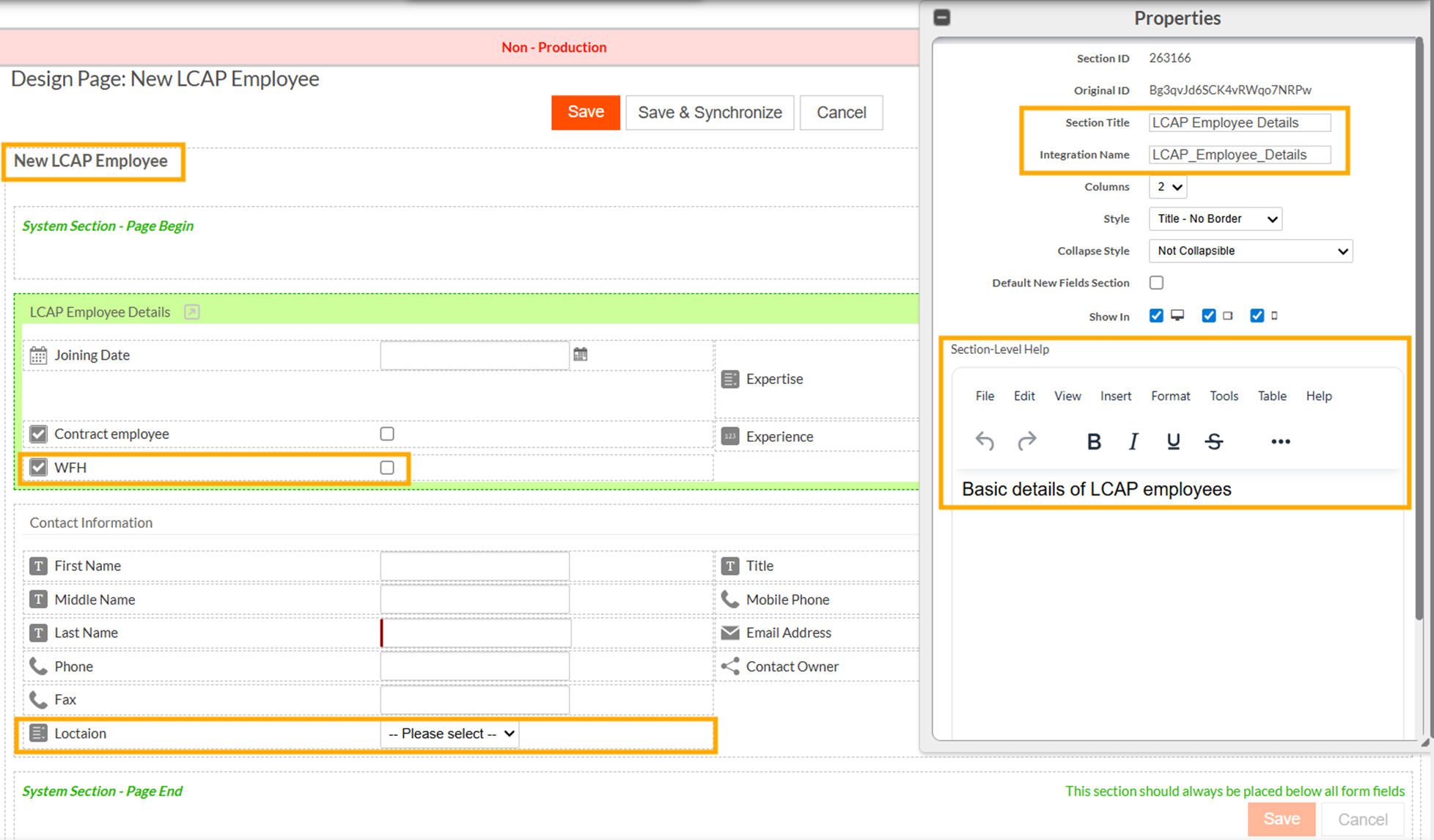
-
After the application update is installed in the destination tenant, the previously applied customizations - such as the one-column layout for the Employee Details section, remains intact. At the same time, the destination also receives important updates from the source, including the updated section integration name and the newly added fields.
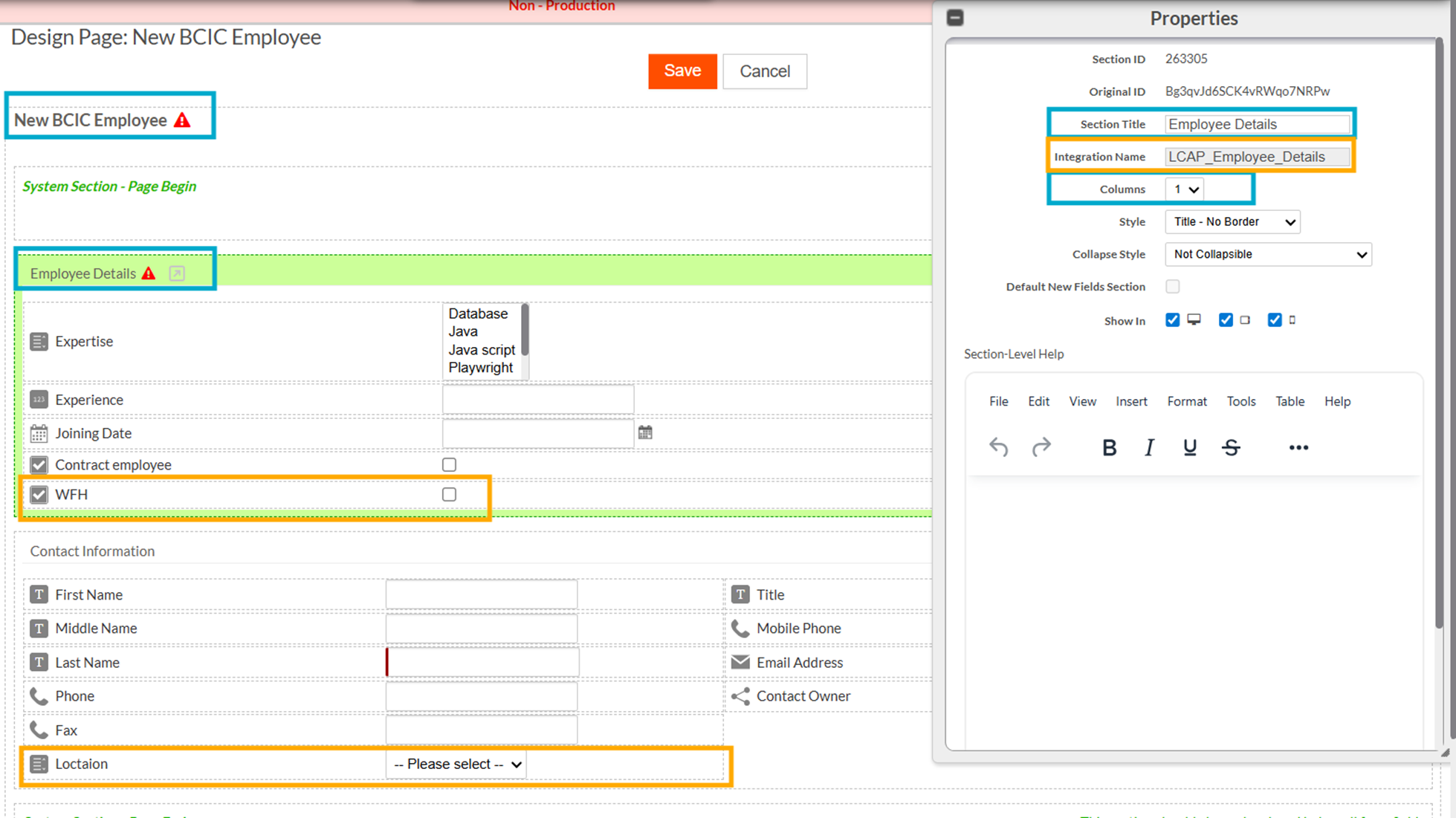
This demonstrates how the framework preserves tenant-level flexibility while still applying critical source updates, ensuring a seamless and balanced upgrade process.

