External object fields and attributes
There is a fundamental difference between the way new fields are created for external objects and the way they are created for native Platform objects. In the latter case, new fields can be created either through enabling a new object attribute (such as Contact or Location) or by creating a field manually in the Platform user interface.
External objects are stored in an existing table with a structure which cannot be modified. For this reason, new fields in external objects can only be created in one of the following cases:
- They rely on a column in the external table that exists, but has not yet been mapped to a Platform field in that external object.
- They do not require a database column in the external table to store data, such as: formulas, templates, roll-up Summary, and integration links.
The field configuration process is almost identical to native Platform object fields. As usual, newly created fields on external objects can be added to pages, views, reports, and referenced anywhere normal object fields can be, such as in formulas, templates, triggers, and validations. Creation or deletion of a field in an external table will most likely require modifying the SQL queries as described in SQL queries for external objects. For your convenience, the system will redirect you to the Adjust SQL page after a field is created or deleted.
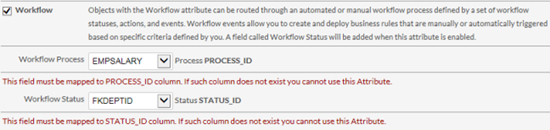
You can assign object attributes by mapping fields from particular attribute (such as Contact) to an available data column. If an attribute box is checked for an external object, all of its fields must be mapped and no column can be mapped to more than one field. Some fields must be mapped to columns with a specific name. For example, a workflow Status must be mapped to a column named STATUS_ID.